- mc@endowien.at
- +43 1 503 07 06
- +43 699 172 347 83
- Bösendorfer Street 6 / 3rd Floor / Door 17, 1010 Vienna
Wann ist eine Revision erforderlich?
A tooth has already been root-treated. If germs remained in the tooth, they can later cause chronic or even acute inflammation at the root tip. In the X-ray, we may see that the root treatment has been performed, but there could also be a new or not fully healed old infection. The existing root filling might appear uneven (heterogeneous) or too short in the X-ray. In such cases, bacteria likely remained in the cavities, causing the inflammation. In this case, the old, unsuccessful root treatment must be revised so that the infection can be eliminated. This way, the "time bomb" can be defused, and the tooth can be preserved long-term.
Complications in the healing process may be caused by:
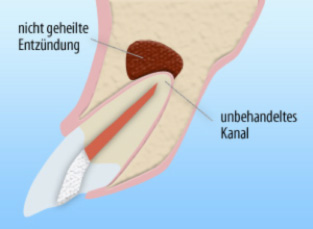
In some cases, other issues can negatively affect the tooth:
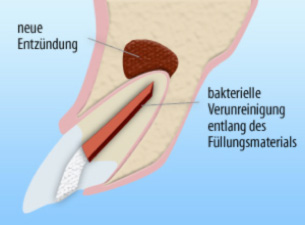
How much will this treatment cost?
The cost depends on how complicated the treatment is. A revision is more complicated than an initial treatment. There are several reasons for this:
What other options do I have?
Bitte füllen Sie das Formular aus, um schnellstmöglich einen Termin zu erhalten.